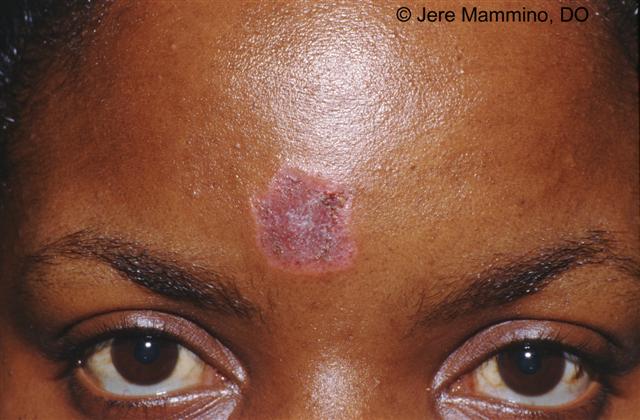
Skin Cancer Causes Biography
Source(google.com.pk)Cancer is a class of diseases characterized by out-of-control cell growth. There are over 100 different types of cancer, and each is classified by the type of cell that is initially affected.
Cancer harms the body when damaged cells divide uncontrollably to form lumps or masses of tissue called tumors (except in the case of leukemia where cancer prohibits normal blood function by abnormal cell division in the blood stream). Tumors can grow and interfere with the digestive, nervous, and circulatory systems, and they can release hormones that alter body function. Tumors that stay in one spot and demonstrate limited growth are generally considered to be benign.
Cancer cell
More dangerous, or malignant, tumors form when two things occur:
a cancerous cell manages to move throughout the body using the blood or lymph systems, destroying healthy tissue in a process called invasion
that cell manages to divide and grow, making new blood vessels to feed itself in a process called angiogenesis.
When a tumor successfully spreads to other parts of the body and grows, invading and destroying other healthy tissues, it is said to have metastasized. This process itself is called metastasis, and the result is a serious condition that is very difficult to treat.
How cancer spreads - scientists reported in Nature Communications (October 2012 issue) that they have discovered an important clue as to why cancer cells spread. It has something to do with their adhesion (stickiness) properties. Certain molecular interactions between cells and the scaffolding that holds them in place (extracellular matrix) cause them to become unstuck at the original tumor site, they become dislodged, move on and then reattach themselves at a new site.
The researchers say this discovery is important because cancer mortality is mainly due to metastatic tumors, those that grow from cells that have traveled from their original site to another part of the body. Only 10% of cancer deaths are caused by the primary tumors.
The scientists, from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, say that finding a way to stop cancer cells from sticking to new sites could interfere with metastatic disease, and halt the growth of secondary tumors.
In 2007, cancer claimed the lives of about 7.6 million people in the world. Physicians and researchers who specialize in the study, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of cancer are called oncologists.
Malignant cells are more agile than non-malignant ones - scientists from the Physical Sciences-Oncology Centers, USA, reported in the journal Scientific Reports (April 2013 issue) that malignant cells are much “nimbler” than non-malignant ones. Malignant cells can pass more easily through smaller gaps, as well as applying a much greater force on their environment compared to other cells.
Professor Robert Austin and team created a new catalogue of the physical and chemical features of cancerous cells with over 100 scientists from 20 different centers across the United States.
The authors believe their catalogue will help oncologists detect cancerous cells in patients early on, thus preventing the spread of the disease to other parts of the body.
Prof. Austin said "By bringing together different types of experimental expertise to systematically compare metastatic and non-metastatic cells, we have advanced our knowledge of how metastasis occurs."
What causes cancer?
Cancer is ultimately the result of cells that uncontrollably grow and do not die. Normal cells in the body follow an orderly path of growth, division, and death. Programmed cell death is called apoptosis, and when this process breaks down, cancer begins to form. Unlike regular cells, cancer cells do not experience programmatic death and instead continue to grow and divide. This leads to a mass of abnormal cells that grows out of control.
What is cancer? - Video
A short, 3D, animated introduction to cancer. This was originally created by BioDigital Systems and used in the Stand Up 2 Cancer telethon.
Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
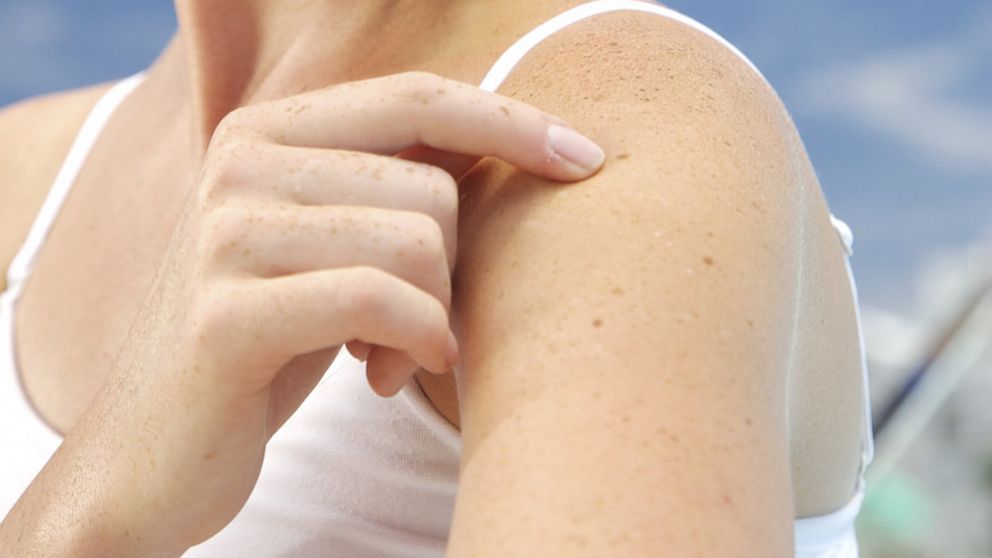
Skin Cancer Causes Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics