Different Types Of Skin Cancer Biography
Source(google.com.pk)Normally the body's cells grow and divide in an orderly way. New cells replace old and damaged cells, so that tissue can grow and heal itself.
Sometimes cells act abnormally because of damaged genes in their nuclei. Such cells grow faster than those around them. They don't develop the features and activities of normal cells.
Scientists believe that tumors begin as a single cell with genetic damage. The cell then begins replicating itself. The damage passes from one generation to the next with each cell division. The cells grow into a lump, or tumor.
Two Kinds of Tumors
There are two basic types of tumors:
benign (non-cancerous)
malignant (cancerous)
Benign Tumors
Benign, or non-cancerous, tumors do not spread beyond defined boundaries.
Malignant Tumors
Malignant, or cancerous, tumors have no boundaries. Their cells push between surrounding cells. Cells of malignant tumors can also spread, or metastasize, throughout the body. These cells break from the tumor and travel in the blood or lymph. They eventually get into surrounding tissues or other parts of the body. There they form secondary tumors.
Not all cancers form solid tumors. Leukemia is the general name used for cancers of the white blood cells or leukocytes. Leukemias do not form solid tumors.
Back to Top
What Exactly Is "Cancer?"
Cancer is not a single disease. It is an overall term given to many different diseases.
In all cancers:
A cell's genes are damaged, or mutated. This causes uncontrolled cell division.
Mutated cells can't do the things normal cells do. Plus, the mutated cells begin to crowd out healthy cells and steal nutrients from them. Carcinogens are chemical, physical, or biological agents that damage a cell's DNA. This damage can lead to cancer.
Certain carcinogens are linked to certain cancers. For example, tobacco is linked to lung cancer. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is linked to skin cancer. Sixty-five to eighty percent of skin cancers are caused by too much exposure to the sun's UV rays.
How Genes Control Cell Division
Our body is made up of trillions of cells. Some cells, such as skin cells, divide quickly to replace those that die and are sloughed off the surface. Other cells, such as nerve cells, may never divide.
There are two types of genes that control the rate at which cells divide:
growth-promoting genes
tumor suppressor genes
Growth-promoting genes turn cells "on" and stimulate cell growth and division. Tumor suppressor genes turn cells "off" and block cell growth and division. These two types of genes are the main targets of genetic damage. Damage to a growth-promoting gene can cause it to remain turned on. This can lead to tumor formation. A tumor may also form if a suppressor gene is damaged and fails to turn a cell off.
The Role of the p53 Gene
In 1990, scientists found a tumor suppressor gene known as the p53 gene. This gene is the most common target for mutations in human cancers. It is found on chromosome 17.
Mutations of p53 have been found in many different cancers including breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, and skin cancer. Scientists think that the p53 gene blocks replication of mutated DNA. So p53 is considered a "tumor suppressor gene." When DNA is damaged, the cell senses that damage and activates the p53 gene.
When p53 doesn't do its job, damaged DNA can replicate, and tumors may form.
The Two-Hit Theory
Most people are born with two working copies of the p53 gene in each cell. (One copy is on the chromosome 17 from the mother. The other is on the chromosome 17 from the father.) Cancer probably won't result if only one copy of p53 is damaged by a carcinogen, such as UV radiation. But if both copies are damaged, mutated DNA can replicate. Then cancer can result. This is called the "two-hit theory" of cancer development.
Some p53 mutations can be inherited. Let's say someone is born with one working and one mutated copy of p53. What might happen if that person is exposed to a "second hit" by a carcinogen such as UV radiation? How is their cancer risk different from that of someone born with two working copies of p53?
Back to Top
Exercises
Questions
Cells double in number each time they divide. How many times must a cell divide to produce 100,000 cells?
Give two reasons why cells normally divide.
Which part of the cell controls cell division?
What can happen if this part of the cell is damaged?
How is a cancer cell different from a normal cell?
Explain the difference between a benign tumor and a malignant tumor.
How can cancer cells spread throughout the body?
True or False
The purpose of cell division is for growth and tissue repair.
The mitochondria controls cell division.
Abnormally fast cell growth is called cancer.
A tumor that does not spread is termed "malignant."
An antigen is a substance that causes cancer.
Too much exposure to sunlight can cause skin cancer.
Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
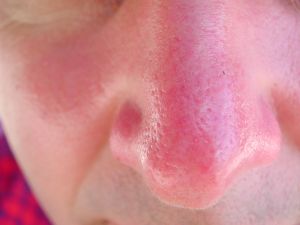
Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
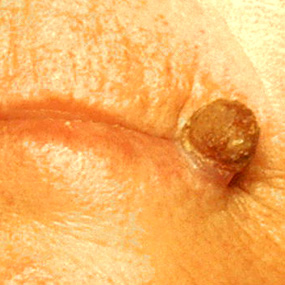
Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics


Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics

Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics


Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
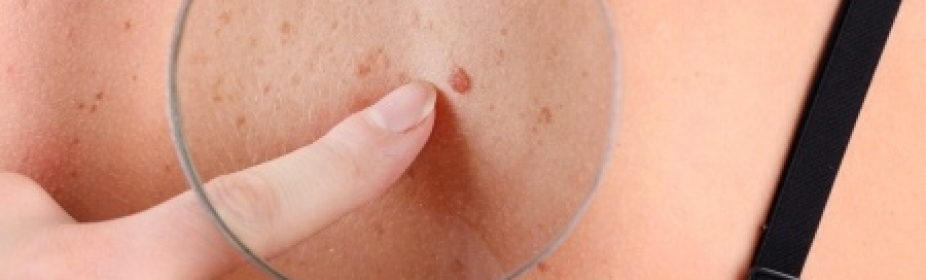

Different Types Of Skin Cancer Skin Cancer Pictures Moles Symptoms Sings On Face Spots On Nose Photos Types Pics Wallpapers Pics
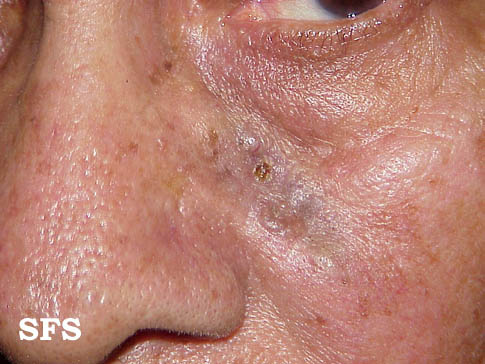
No comments:
Post a Comment